How to Choose a Gaming Motherboard
April 25,2022
Choosing a gaming motherboard is a hugely important part of building a PC.
What does a motherboard do? It’s the circuit board that connects all of your hardware to your processor, distributes electricity from your power supply, and defines the types of storage devices, memory modules, and graphics cards (among other expansion cards) that can connect to your PC.
Below, we’ll dive into motherboard anatomy and give you all the information you need to learn how to choose a motherboard for your build.
Motherboard Anatomy
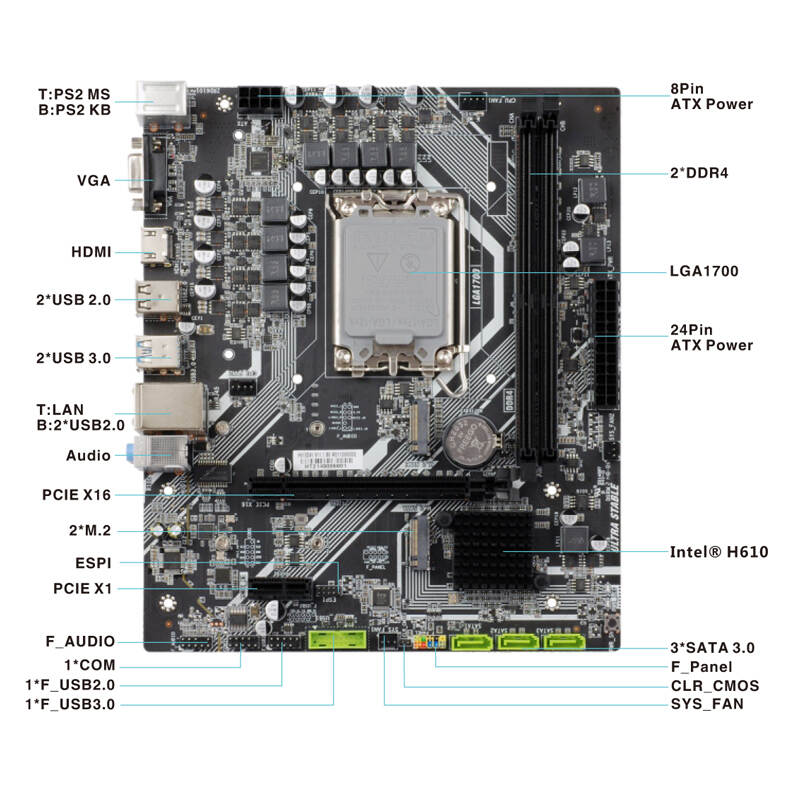
A motherboard is a PC’s primary circuit board. Though motherboard aesthetics change over time, their basic design makes it easy to connect new expansion cards, hard drives, and memory modules, as well as replace old ones.
Let’s walk through some of the terms you’ll encounter when comparing motherboards.
Motherboards usually contain at least one processor socket, enabling your CPU (the PC’s mechanical “brain”) to communicate with other critical components. These include memory (RAM), storage, and other devices installed in expansion slots — both internal devices like GPUs and external devices like peripherals.
(Not all motherboards have a socket, though: in systems with less space, like Intel® NUC and most laptops, the CPU is soldered into the motherboard.)
When selecting a motherboard, check your CPU’s documentation to ensure the board is compatible with your CPU. Sockets vary in order to support different products based on generation, performance, and other factors by changing the pin array. (The name of the socket comes from the pin array: for example, the LGA 1151 socket, compatible with 9th Gen CPUs, has 1,151 pins.)
Modern Intel motherboards connect CPUs directly to RAM, from which it fetches instructions from different programs, as well as to some expansion slots that can hold performance-critical components such as GPUs and storage drives. The memory controller lives on the CPU itself, but numerous other devices communicate with the CPU through the chipset, which controls many expansion slots, SATA connections, USB ports, and sound and network functions.
How do processor sockets work?
Chipset
The chipset is a silicon backbone integrated into the motherboard that works with specific CPU generations. It relays communications between the CPU and the many connected storage and expansion devices.
While the CPU connects directly to RAM (via its built-in memory controller) and to a limited number of PCIe* lanes (expansion slots), the chipset acts as a hub that controls the other buses on the motherboard: additional PCIe lanes, storage devices, external ports like USB slots, and many peripherals.
Higher-end chipsets can feature more PCIe slots and USB ports than standard models, as well as newer hardware configurations and different allocations of PCIe slots (with more linked directly to the CPU).
Click to learn more about chipsets and the platform controller hub (PCH)
Choosing a Chipset
Modern chipsets consolidate many features that were once discrete components connected to motherboards. Onboard audio, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth®1 technology, and even cryptographic firmware are now integrated into Intel chipsets.
High-end chipsets like Z390 can offer many benefits, including overclocking support, and higher bus speeds. But Intel chipsets also provide further improvements.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the differences between Intel’s chipset series:
Z-Series
Overclocking support for CPUs with “K” designation
Maximum of 24 PCIe lanes
Up to six USB 3.1 Gen 2 ports
Maximum of 24 PCIe lanes
Up to six USB 3.1 Gen 2 ports
H-Series
No overclocking support
Maximum of 20 PCIe lanes
Up to four USB 3.1 Gen 2 ports
Maximum of 20 PCIe lanes
Up to four USB 3.1 Gen 2 ports
B-Series
No overclocking support
Maximum of 20 PCIe lanes
USB 3.0 ports only
These different options enable entry at a variety of price points, while still taking advantage of the benefits of the 300-series chipset.
Make Your Choice
Whether you're planning your next build or upgrading your current gaming PC, understanding the components of your gaming motherboard is crucial. Once you know what everything does, you’ll know how to choose a gaming motherboard that suits your build.
You need a socket that matches your CPU, a chipset that maximizes the potential of your hardware, and finally a feature set that matches your computing needs. Take the time to list out several compatible motherboards and compare their key advantages before making a decision, and you should find exactly what you are looking for.